
For temporary accounts, automation simplifies the process of closing and resetting balances at the end of each accounting period. Automated systems can generate and post closing entries, transfer balances to permanent accounts, and prepare the necessary financial reports with minimal manual intervention. Inconsistent accounting practices can also lead to challenges in managing temporary and permanent accounts. It’s crucial to establish and maintain consistent accounting practices to ensure accurate financial reporting. Consistency in accounting practices helps businesses to track financial transactions accurately, identify discrepancies, and make informed decisions.
Temporary Account Examples
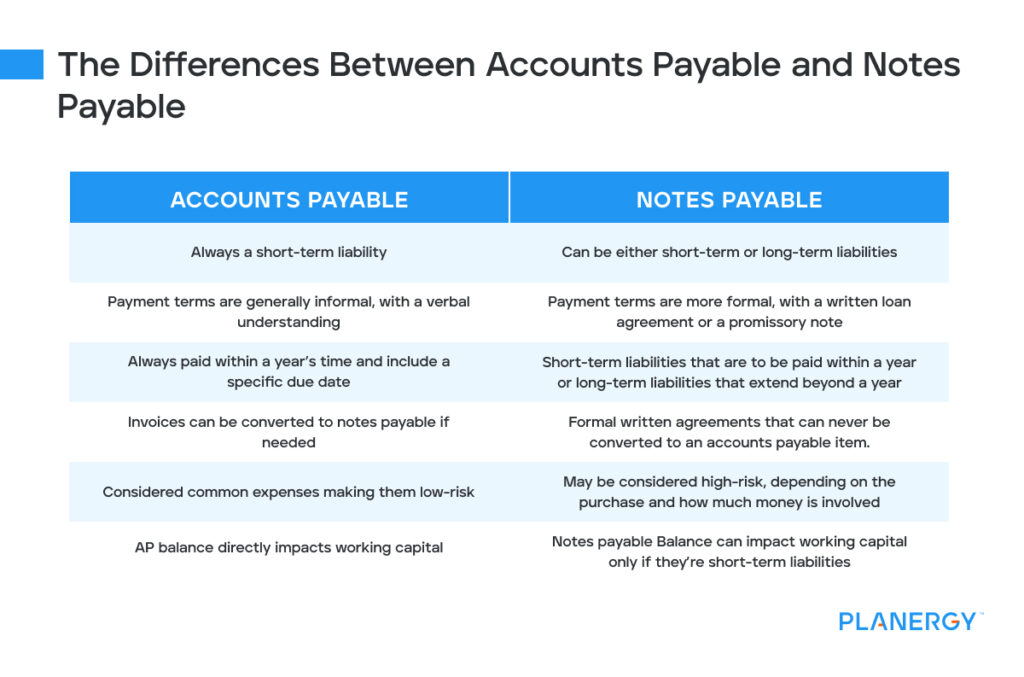
On the maturity date, only the Note Payable account is debited for the principal amount. A business may borrow money from a bank, vendor, or individual to finance operations on a temporary or long-term basis or to purchase assets. Note Payable is used to keep track of amounts that are owed as short-term or long- term business is notes payable a permanent or temporary account loans. The company obtains a loan of $100,000 against a note with a face value of $102,250. The difference between the face value of the note and the loan obtained against it is debited to discount on notes payable. Dividends paid to shareholders are also recorded in a temporary account, specifically the dividend account.
Asset accounts
If the payment was made on June 1 for a future month (for example, July) the debit would go to the asset account Prepaid Rent. The note payable is a written promissory note in which the maker of the note makes an unconditional promise to pay a certain amount of money after a certain predetermined period of time or on demand. The purpose of issuing a note payable is to obtain loan form a lender (i.e., banks or other financial institution) or buy something on credit.
FAR CPA Practice Questions: Calculating Interest Expense for Bonds Payable
- Under the accrual basis of accounting, the matching is NOT based on the date that the expenses are paid.
- Expenses normally have debit balances that are increased with a debit entry.
- Automated reconciliation tools compare account balances against external statements or records, ensuring that discrepancies are identified and resolved efficiently.
- At the end of the period, balances from these accounts are transferred to the income summary account.
- The premium or discount amount is to be amortized over the term of the note.
Likewise, lenders record the business’s written promise to pay back funds in their notes receivable. At some point or another, you may turn to a lender to borrow funds and need to eventually repay them. Learn all about notes payable in accounting and recording notes payable in your business’s books. Equity accounts represent the residual interest in the assets of an entity after deducting liabilities.
At the end of the period, the balances in these accounts are closed and transferred to retained earnings or capital. Accounts payable are short-term liabilities that a company owes to its vendors or suppliers due to the credit purchase of goods and services. This money is paid back to maintain good working relationships and establish creditworhthiness with suppliers. Accounts payable are recorded as a current liability on the company’s balance sheet. Permanent accounts allow businesses to track their financial progress over time since these account balances carry forward from one period to the next.
As a result, income statement accounts are transient and must be closed on a regular basis. This is a non-operating or “other” item resulting from the sale of an asset (other than inventory) for more than the amount shown in the company’s accounting records. The gain is the difference between the proceeds from the sale and the carrying amount shown on the company’s books. Revenues and gains are recorded in accounts such as Sales, Service Revenues, Interest Revenues (or Interest Income), and Gain on Sale of Assets.
In accounting, temporary accounts are used to record financial transactions for a particular accounting period. All temporary account balances must be moved to permanent accounts at the end of the time. Among its many complexities are the accounts used for categorizing the flow of money. Most business owners are familiar with the core account types, such as revenue and expenses.
For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) hasworked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. For the past 52 years, Harold Averkamp (CPA, MBA) has worked as an accounting supervisor, manager, consultant, university instructor, and innovator in teaching accounting online. The premium or discount amount is to be amortized over the term of the note.
Read on to learn the difference between temporary vs. permanent accounts, examples of each, and how they impact your small business. Asset accounts – asset accounts such as Cash, Accounts Receivable, Inventories, Prepaid Expenses, Furniture and Fixtures, etc. are all permanent accounts. Contra-asset accounts such as Allowance for Bad Debts and Accumulated Depreciation are also permanent accounts. Sales are reported in the accounting period in which title to the merchandise was transferred from the seller to the buyer.
Uncover why real-time data is essential for an efficient continuous close process. It also provides valuable tools that help manage customer information, monitor payment records, and create proper billing and collection reports. As a result, invoice and billing management are simple and convenient. You also get access to active customer support, ready to assist you whenever you need help. If you’re a solo proprietor or your company is a partnership, you’ll need to shift activity from your drawing account for any excises received from the company. Expense accounts, such as Cost of Sales, Interest, Rent, Delivery, Utilities, and any other expenses, are transitory accounts.
As a result, every time a new period begins, a temporary account’s balance is reset to 0. There are no further transactions in these accounts since their balances have been separated for this accounting period. The goal is to display the produced earnings as well as the accounting activities for each period. Long-term notes payable are often paid back in periodic payments of equal amounts, called installments.